Attention Model
14 minutesBasic Concepts of the Attention Mechanism
The attention mechanism is a widely used technique in deep learning. As its name suggests, attention allows a model to “focus” on the most relevant parts of the input data by assigning higher weights to important features. This helps stabilize gradients when training deep models and improves overall performance across tasks such as machine translation, image understanding, and speech processing.
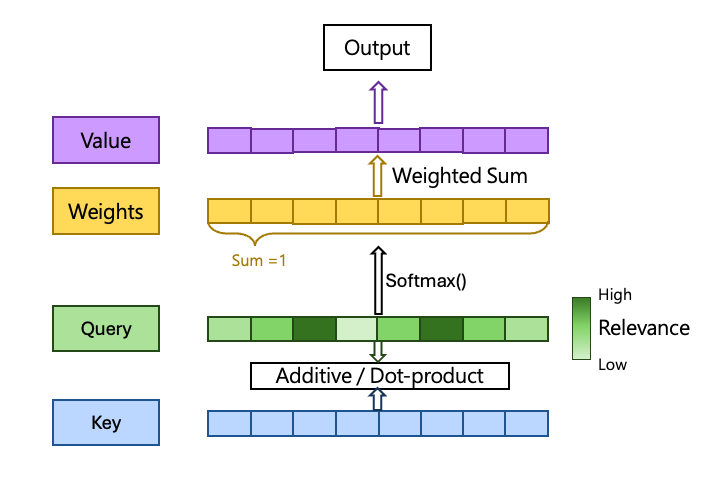
In a standard attention architecture, there are three key components: Query, Key, and Value.
Query(Q)
A Query can be viewed as the model’s “question.”
It is a vector representing what the model is trying to look for—capturing the relationship between the input and the desired output.
Key (K)
A Key is a vector associated with the input data (e.g., a word in a sentence or a feature in an image).
In the first step of attention, the model computes a similarity score between the Query and each Key—commonly using additive similarity or dot-product similarity.
These similarity scores are then normalized using a function such as Softmax to form weights that sum to 1.
Value (V)
The Value represents the actual content or information carried by the input.
By applying the attention weights to the Values, the model produces a weighted sum, which becomes the final output passed to subsequent layers.
Practical Applications of Attention Models
See also: CLAM
Attention mechanisms are particularly useful for identifying the most informative regions in whole slide images (WSIs).
Because WSIs contain highly heterogeneous and complex tissue structures, attention helps the model focus on the truly meaningful cells or regions, leading to improved accuracy in histopathology image analysis.
